Beschreibung
3D Scanning Output
What are the WorkFlow and Outputs of 3D Scanning?
Every 3D Scan Project that we undertake is evaluated for success…
we can scan items from 100mm* to 600mm* cubic (Xmm by * Xmm * by Xmm)
deliver your item to our studio
it takes 5-10 days to fit your scan into our workflow
we may chose to use 3d structured light scanning or 3d photogrammetry scanning
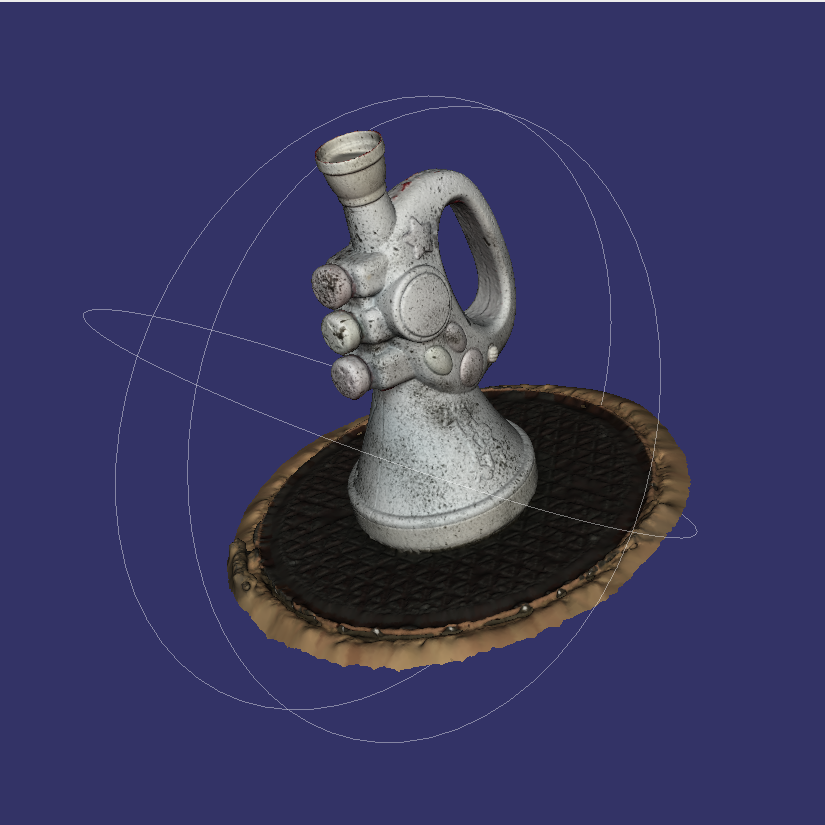
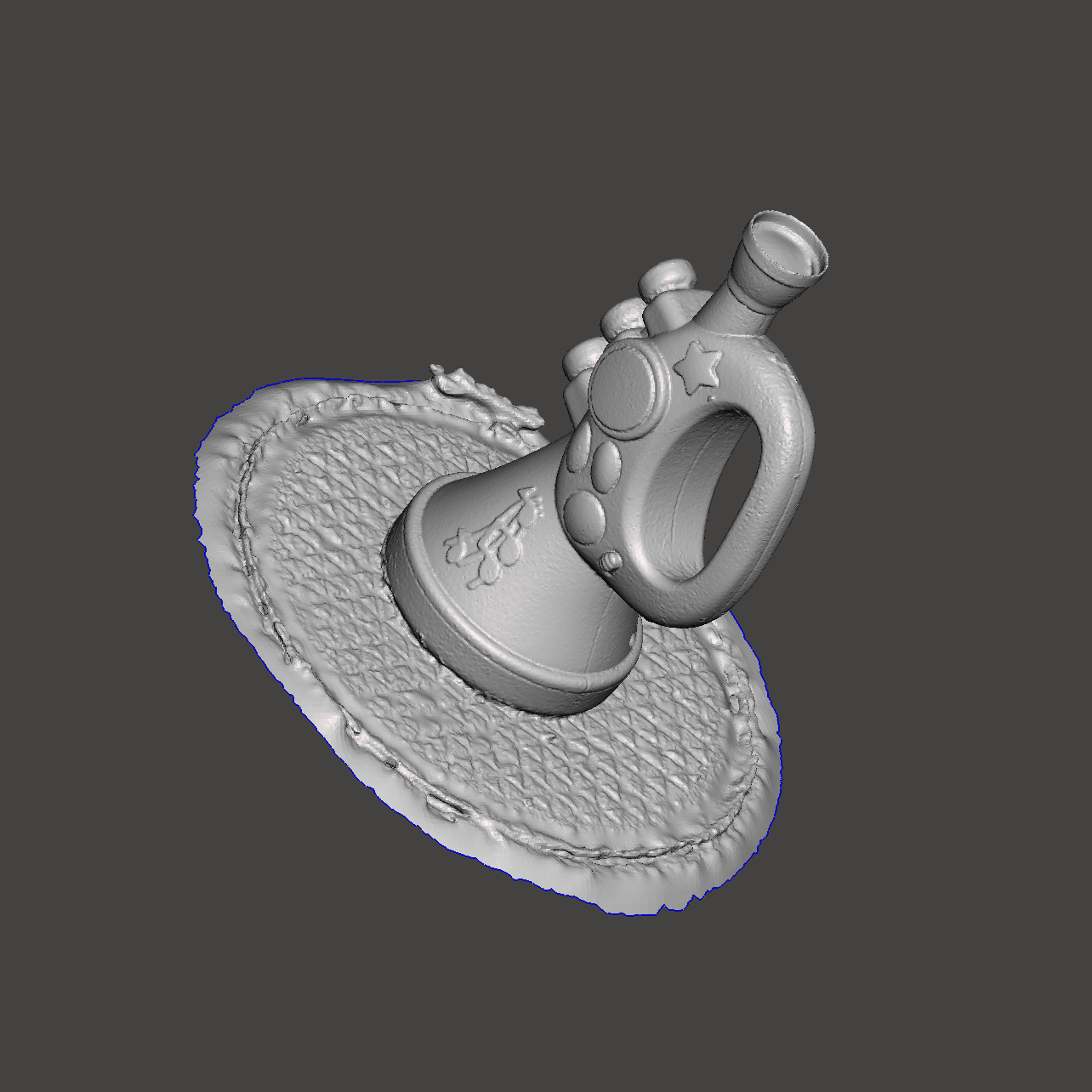
the resulting file is a 3D point cloud of data
to get to a usable CAD or 3D Printing file you will require additional chargeable time to reverse-engineer this 3D point cloud into a usable CAD file, this can take days depending on the complexity of your object. You may choose to do this yourself, many customers do.
3D Scanning can help create 3D Computer Model files for use in 3D Printing.
Using a fine Laser or a Light grid we can scan the surface of an item from many angles to generate the 3D shape in the computer.
3D data is generated like radar or sonar, to detect an object’s surface and features from a known location [the scanner].
Photogrammetry:
The science of making measurements from photographs.
Retopology:
Recreating an existing surface with more optimal geometry.
Scanning using structured light 3D technology.
3D Scanning is computationally intensive (time to process the scanned data) so it is best to decide which is quicker and therefore more cost-effective or more precise; 3D Scanning or 3D CAD Modelling.
Creating a 3D Scan can be the best option for objects where the exact detailed* recreation of complex compound curves or surface textures are required (patterns, text, inscriptions), which is not humanly or economically possible to recreate.
3D Photogrammetry
q. ‘Photogrammetry is the science of making measurements from photographs. The input to photogrammetry is photographs, and the output is typically a map, a drawing, a measurement, or a 3D model of some real-world object or scene.’
3D Structured Light
q. ‘Structured-light 3D scanners project a pattern of light on the subject and look at the deformation of the pattern on the subject. The pattern is projected onto the subject using either an LCD projector or another stable light source. A camera, offset slightly from the pattern projector, looks at the shape of the pattern and calculates the distance of every point in the field of view.’
3D Scanning Uses
An example of such detailed* shapes are;
museum artefacts
sculpted artworks
statues, or
unavailable / discontinued plastic or metal components
*’Detail’ can be down to 0.04 mm resolution.
At best a human can 3D Sculpt a close approximation but it will not be as exact or dimensionally perfect as a computational Scan.
Scanning Note
We curently only supply Photogrammetry as a Pont Cloud STL model for you to use for your own Reverse-Engineering.