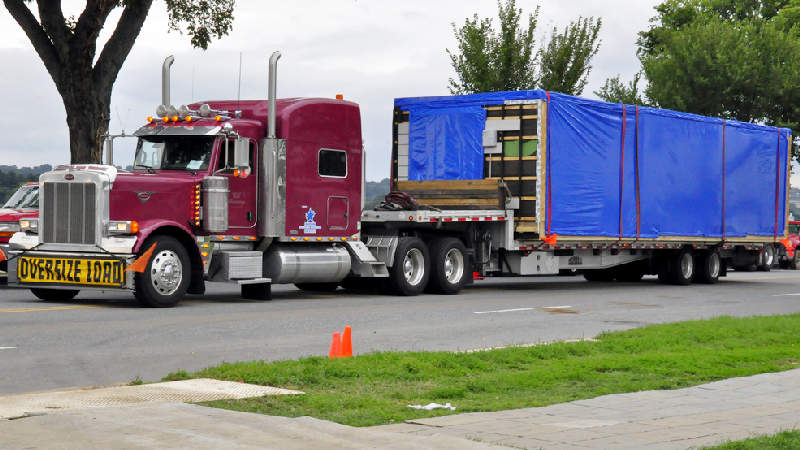
Modular homes, as the title suggests, are always created in modules (2-4 or more) using traditional materials. After transporting to the place of installation, the parts are assembled together like a giant construction kit on a permanent foundation. They are built to local code as determined by the local jurisdiction, the same as site-built houses. Modular homes in general are treated as regular real estate and it shouldn’t be confused with manufactured homes.
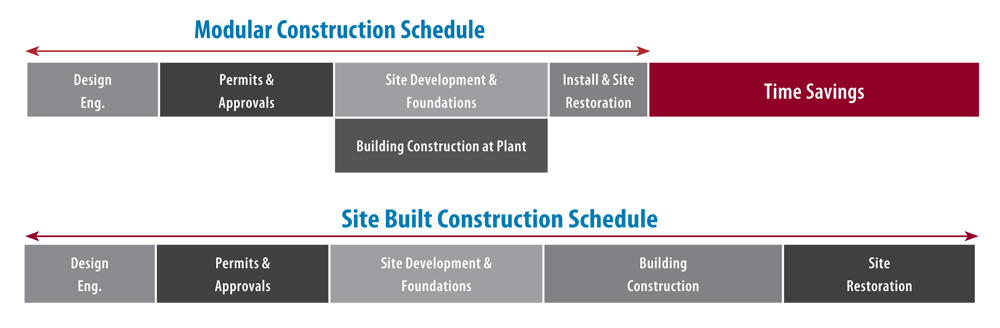
One of the main advantages with buying modular homes is that you can reduce construction time by more than one third in comparison to traditional methods. As a rule, it takes about a week to complete the installation of a modular home. The parts for modular homes look like box-shaped modules, which are then assembled with each other on the construction site. Modular homes can be multi-stories high and are attached to each other on-site. The sections are transported on flatbed trucks so they are usually up to 16 ft wide (about 4.9 meters). Modular homes can look identical to traditional frame site-built homes once fully assembled.
Are modular homes safe?
There are plenty of fears around buying prefabricated homes, and modular homes are no exception. One of the main questions that everyone should ask is: are they hurricane-proof? You might be surprised to find out that modular homes resist extreme conditions much better than traditional ones.
Federal Emergency Management Agency has approved manufactured (here is a link) and modular homes for excellent quality. After Hurricane Andrew hit Florida in 1993, they reported that modular homes “performed much better than conventional residential framing.” Furthermore, all modules are transported on flatbed trucks with an average speed of up to 60 miles per hour, so all the parts are made with an additional safety margin.
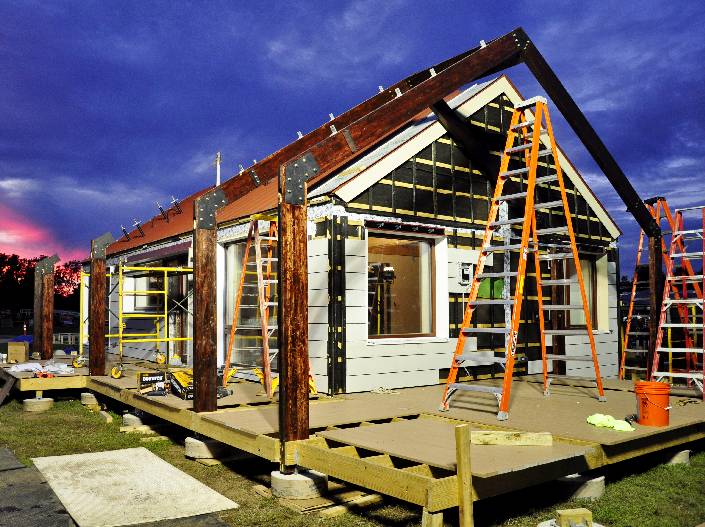

Building codes for modular homes
Differences include the building codes that govern the construction, types of material used and how they are appraised by banks for lending purposes. The laws that govern the development of modular homes are exactly the same codes that govern the building of site-constructed dwellings. In the United States, all modular homes are constructed according to the International Building Code (IBC), IRC, BOCA, or the code that has been adopted by the local jurisdiction.
Materials that are used in modular building
The materials used in modular homes are typically the same as site constructed homes. Wood-frame floors, walls, and roofs are often used. Some modular homes include brick or stone exteriors, granite counters, and steeply pitched roofs. Modulars can be designed to sit on a perimeter foundation or basement and can be custom built to a client's specifications. Current designs include multi-story units, multi-family units, and entire apartment complexes.
How much do modular homes cost?
The price can vary from as low as $50k to millions of dollars. You can generally expect to spend anywhere from 10 to 20% less on your home if you choose to live in the modular house. These savings are found mostly in three major areas: bulk purchasing, labor costs, and building materials. The value can depend on many factors, like location and additional customization. Be aware that in the end, you’ll have to pay more than you calculated. According to the Definitive Guide to Building Modular, there are five different prices that may be used to quote the modular home's cost:
- The base price (includes only the cost of manufacturing the modules without customizations and alterations)
- The custom price (consists of the base price + appropriate finishes and chosen upgrades)
- The delivered price (the amount of manufacturing the house + delivery and setting up with fastening the modules to each other and attaching roofs and dormers, but will not include any additional roofing work, connecting utilities)
- The finished price (includes everything the previous prices do in addition to the estimated costs for site prep, pouring the foundation, buttoning up, and any site works like constructing porches).
- The all-in price
What are the pros and cons of modular homes?
We summed up the most important advantages and disadvantages of modular homes. They can vary depending on its price and class.
Advantages of modular houses
- Modular homes, like traditional site-built homes, are financed with a mortgage
- Modular homes typically cost 10-20% less than the traditionally-constructed equivalent
- The speed of construction. It also reduces labor costs.
- Indoor construction. Assembly is independent of weather, which can increase work efficiency and avoids damaging building material.
- No problems with construction waste
- Flexibility - one can continually add to a modular building. When the needs change, modular buildings can be disassembled, and the modules relocated or refurbished for their next use reducing the demand for raw materials and minimizing the amount of energy expended to create a building to meet the new need.
- Quality - due to the need to transport modules to the final site, each module must be built to withstand travel and installation requirements independently. Thus, the final module-to-module assembly of alone durable components can yield a final product that is more durable than site-built structures.
Disadvantages of modular houses
- Cautious attitude of some realtors and buyers
- Some financial institutions may be hesitant to offer a loan for a modular home.
Top guides
Photos by Team Massachusetts 4D Home
Mit Freunden teilen: